Cellular Membranes
Abstract
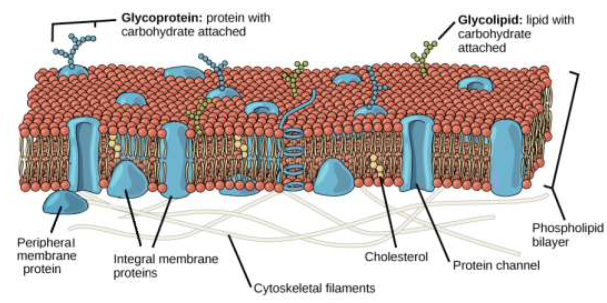
Cellular membranes serve as an effective partition between the cell and its environment, while intracellular membranes compartmentalize cells. Compartmentalization organizes the cell components and improves efficiency. Biological membranes act as a barrier to most, but not all, molecules. The weak intermolecular forces between membrane components (lipids and proteins) results in continuous breaking and reforming of these attractive forces. The movement of the components and membrane fluidity allows small gaps to form between the components, making biological membranes semi-permeable.
After completing this activity, students will be able to explain noncovalent interactions between components of membranes, the impact of different factors on membrane fluidity, types of movement typical in membranes, and the fluid mosaic model of membranes.
Level: Undergraduate
Environment: Classroom
Activity Type: Learning Cycle
Discipline: Chemistry
Course: Biochemistry
Keywords: membranes, noncovalent forces, lipid bilayer, fluid mosaic model
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright of this work and the permissions granted to users of the PAC are defined in the PAC Activity User License.

